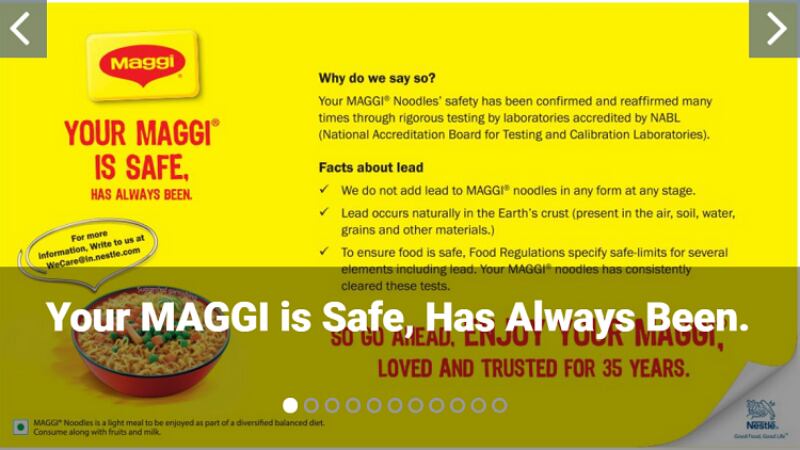
‘No lead in Maggi’: Nestlé India again defends product quality amid lawsuit challenge
Nestlé India has again assured consumers that its Maggi noodles are safe for consumption and do not contain lead, amid an ongoing lawsuit and a reputational crisis that stretches back to 2015.
With regards to the longstanding claims of lead being present in Maggi noodles, Nestlé India insisted that no lead was added to the noodles in any form at any stage in a notice on its official website since last week.
A Nestlé India spokesperson stressed that the Maggi noodles “has been confirmed and reaffirmed many times through rigorous testing by laboratories accredited by National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL).
“To ensure that food is safe, the Food Regulations have specified safe-limits for several elements including lead and Maggi noodles have consistently cleared these tests.
Gluten alert: 3% of Australian on-shelf gluten-free foods found to fail ‘no detectable gluten’ standards
An Australian study has found that 3% of food products claimed to be gluten-free and sold on the shelves of common retail outlets contained detectable levels of gluten.
The researchers identified 256 ‘gluten-free’ items that were most commonly purchased in Australia and were also obtainable from retail outets via a consumer activity database, The Nielsen Company Homescan Online.
Upon obtaining these items, these were homogenised and analysed for gluten presence. The limits set were 5 mg/kg (parts per million, ppm) for quantification and 1 ppm for detection. The relevant manufacturers were quickly informed if detectable gluten was identified.
“Seven samples (~3%) from six manufacturers contained detectable gluten at levels of up to 49 ppm,” said the report.
International requirements: How Japanese food manufacturers can benefit from global food safety guidelines
Japanese food firms have a high understanding of food safety controls, however, most were following their own set of standards and were not familiar with international guidelines, Nigel Asai, HACCP Japan chief, told FoodNavigator-Asia.
This may pose a challenge, as the industry is required to follow the internationally recognised Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) standards by 2020.
Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare announced the mandatory implementation of the HACCP program for the food industry two years ago.
“The food manufacturers in Japan have a high understanding of food safety controls, however, a major issue is that different methods and standards are used,”Asai said.
He believes that following key international standards is necessary for Japanese products to gain international recognition, and this is a key message that he wants to convey to the manufacturing industry.
Adulteration ‘revelation’: 10 out of 10 honey brands tested in India found to violate FSSAI standards
Lab tests have revealed that all 10 out of 10 brands of honey that were tested in India are in violation of Food Safety and Standards Authority (FSSAI) parameters.
The lab tests were conducted by consumer organisation Consumer Voice, who deemed these to be ‘authenticity tests’, and said that the results were a ‘revelation’.
Tests were carried out for C4 sugars (a means of determining whether honey has been adulterated. Pure honey should not contain C4 sugars above certain limits, although this is currently being disputed) as well as a range of other quality, safety and acceptability parameters.
The ten brands of honey tested were: 24 Mantra, Badiyanath, Dabur, Fresh & Pure, Hitkary, Himalaya, Khadi, Patanjali, Reliance and Zandu.
According to FSSAI parameters, C4 sugars should make up no more than 7%. Nearly all of the brands failed the C4 sugar testing.
The top 10 APAC food safety and security stories of 2018
In our year-end round up of the top 10 stories relating to food safety and security in 2018, we recap the Philippines rice crisis, dairy adulteration in India and honey adulteration in Australia and more.